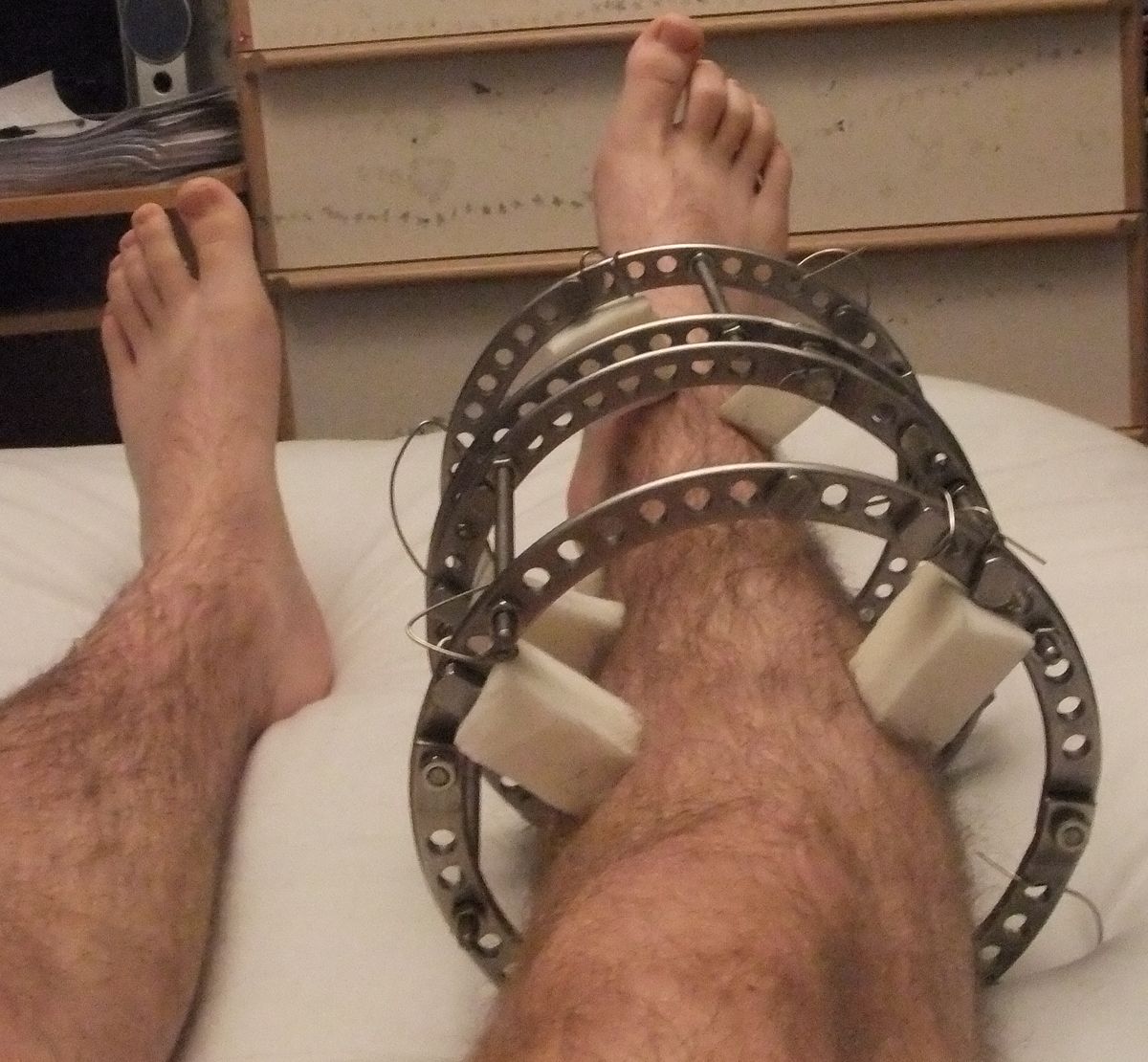
Deformity Correction by Ilizarov Method: A Comprehensive Guide
Deformity correction using the Ilizarov method is a revolutionary orthopedic technique that has transformed the way bone deformities are treated. This method, developed by Soviet orthopedic surgeon Gavriil Ilizarov in the 1950s, utilizes a circular external fixator to gradually correct bone deformities and discrepancies. This comprehensive guide explores the principles, applications, procedure, post-operative care, and advancements related to the Ilizarov method.
Introduction to the Ilizarov Method
The Ilizarov method is based on the principles of distraction osteogenesis, where controlled mechanical distraction stimulates new bone formation. This technique is particularly useful for treating complex deformities, nonunions, and limb length discrepancies that are challenging to address with conventional surgical methods.
Principles of the Ilizarov Method
The Ilizarov method relies on several key principles:
- Tension-Stress Effect: Gradual mechanical distraction under tension stimulates biological processes that promote new bone formation and tissue regeneration.
- Osteogenesis: Bone regeneration occurs through distraction osteogenesis, where bone is cut (osteotomy) and gradually pulled apart, allowing new bone to form in the gap.
- Mechanical Stability: The circular external fixator provides stable support while allowing for micromovements that encourage bone healing.
- Versatility: The modular design of the Ilizarov apparatus allows for precise adjustments and corrections in multiple planes, making it suitable for complex deformities.
Indications for Ilizarov Method
The Ilizarov method is indicated for various conditions, including:
- Congenital Deformities: Such as clubfoot, congenital limb deficiencies, and skeletal dysplasias.
- Post-Traumatic Deformities: Malunions, nonunions, and bone defects resulting from trauma.
- Infectious Conditions: Chronic osteomyelitis with bone defects.
- Limb Length Discrepancies: Significant differences in limb length due to congenital or acquired conditions.
- Joint Contractures: Severe joint stiffness that cannot be corrected by conventional methods.
- Complex Fractures: Open and comminuted fractures that require stable fixation and gradual correction.
Preoperative Planning and Evaluation
Successful deformity correction using the Ilizarov method requires meticulous preoperative planning and evaluation.
Clinical Assessment
- Medical History: Detailed patient history, including previous surgeries, infections, and comorbidities.
- Physical Examination: Assessment of the affected limb, including range of motion, neurovascular status, and skin condition.
- Radiographic Evaluation: X-rays, CT scans, and MRI to assess the extent of deformity, bone quality, and soft tissue status.
Deformity Analysis
- Angular Measurements: Identifying the type and magnitude of angular deformities.
- Rotational Deformities: Assessing rotational malalignment.
- Limb Length Discrepancy: Measuring the difference in limb lengths.
Preoperative Planning
- Osteotomy Site: Determining the optimal site for osteotomy to achieve the desired correction.
- Fixator Configuration: Planning the configuration of the Ilizarov apparatus, including ring size, wire placement, and strut arrangement.
- Distraction Protocol: Establishing a distraction schedule, including the rate and rhythm of distraction.
Surgical Procedure
The Ilizarov surgical procedure involves several key steps:
Anesthesia and Positioning
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia is administered.
- Positioning: The patient is positioned to allow optimal access to the surgical site.
Application of the Ilizarov Apparatus
- Frame Assembly: The Ilizarov apparatus is assembled according to the preoperative plan.
- Wire Insertion: Tensioned wires are inserted through the bone at strategic points to provide stability.
- Ring Placement: Circular rings are attached to the wires and secured to the frame.
Osteotomy
- Incision: A small incision is made at the planned osteotomy site.
- Bone Cutting: The bone is cut using an oscillating saw or a drill, ensuring minimal disruption to the surrounding soft tissues.
- Initial Distraction: A small initial distraction is performed to confirm the mobility of the bone segments.
Gradual Distraction
- Distraction Schedule: Gradual distraction is initiated according to the pre-established schedule, typically at a rate of 1 mm per day, divided into four increments of 0.25 mm.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up visits to monitor progress, adjust the frame, and ensure proper alignment.
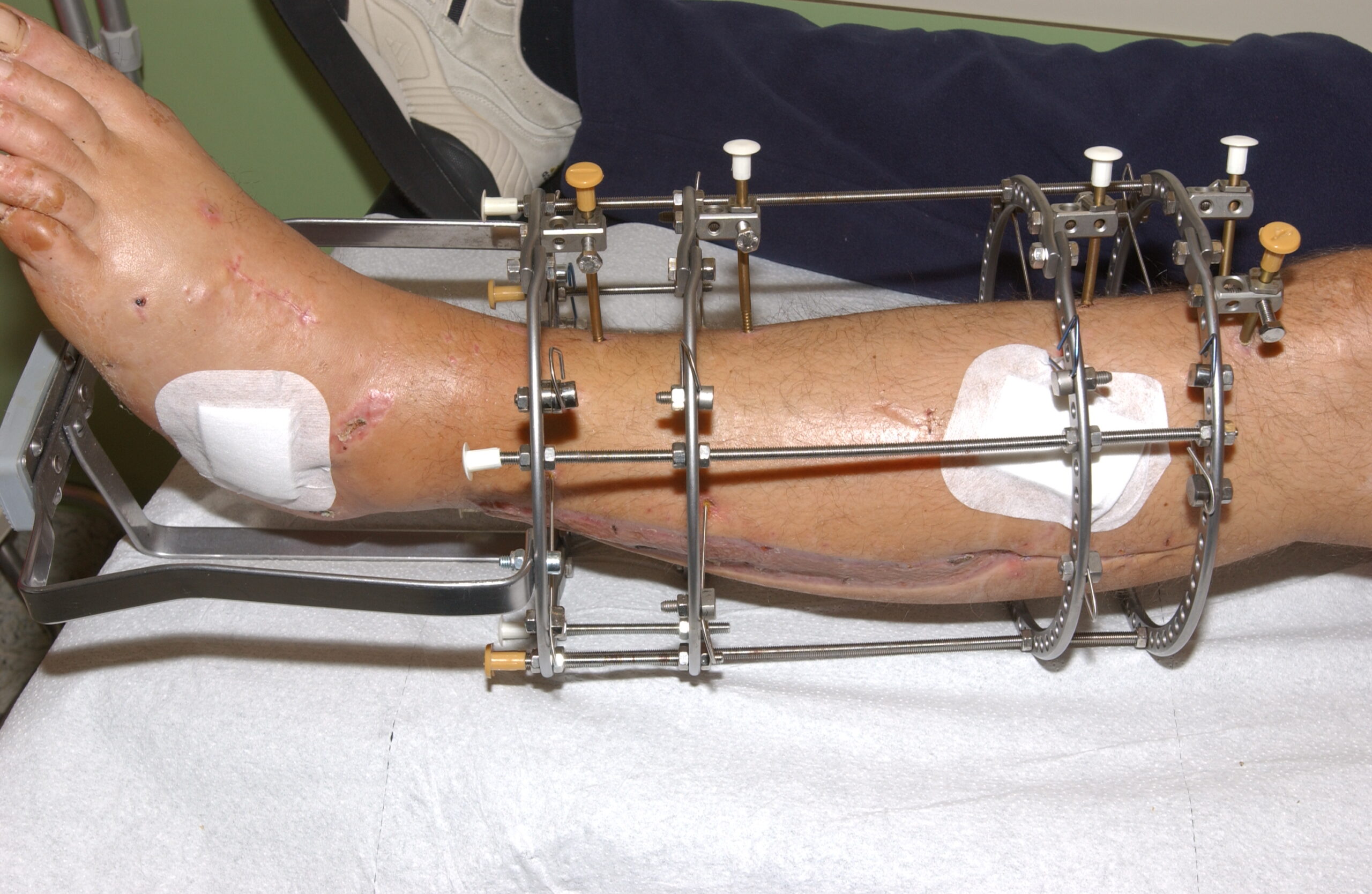
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Postoperative care is critical for the success of the Ilizarov method and involves several key components:
Pain Management
- Medications: Analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications to manage pain and inflammation.
- Non-Pharmacological Methods: Ice therapy, elevation, and relaxation techniques.
Wound Care
- Pin Site Care: Regular cleaning of pin sites to prevent infection, using antiseptic solutions.
- Dressing Changes: Regular changes of dressings to keep the surgical site clean and dry.
Physical Therapy
- Range of Motion Exercises: Early initiation of range of motion exercises to prevent joint stiffness.
- Weight-Bearing: Gradual weight-bearing as tolerated, guided by the physical therapist.
Monitoring and Adjustments
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up visits to monitor progress, adjust the frame, and ensure proper alignment.
- Radiographic Evaluation: Periodic X-rays to assess bone healing and alignment.
Complication Management
- Infections: Prompt treatment of pin site infections with antibiotics and local care.
- Neurovascular Issues: Monitoring for signs of neurovascular compromise and addressing them promptly.
- Mechanical Issues: Addressing mechanical issues with the fixator, such as loosening or breakage of wires and rods.
Advancements in the Ilizarov Method
Over the years, several advancements have been made to enhance the efficacy and safety of the Ilizarov method:
Improved Fixator Designs
- Hybrid Fixators: Combining circular and unilateral fixators for increased stability and versatility.
- Lightweight Materials: Use of lightweight and radiolucent materials to improve patient comfort and ease of radiographic evaluation.
Computer-Assisted Planning
- Software Solutions: Advanced software for deformity analysis and preoperative planning, allowing for precise corrections.
- 3D Printing: Custom 3D-printed models and guides to enhance surgical accuracy.
Biological Enhancements
- Bone Grafting: Use of bone grafts and bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) to enhance bone healing.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Investigating the potential of stem cell therapy to accelerate bone regeneration.
Minimally Invasive Techniques
- Percutaneous Osteotomy: Minimally invasive osteotomy techniques to reduce soft tissue damage and improve recovery times.
- Endoscopic Assistance: Use of endoscopic assistance for precise placement of wires and osteotomies.
Case Studies and Clinical Outcomes
Case Study 1: Congenital Tibial Hemimelia
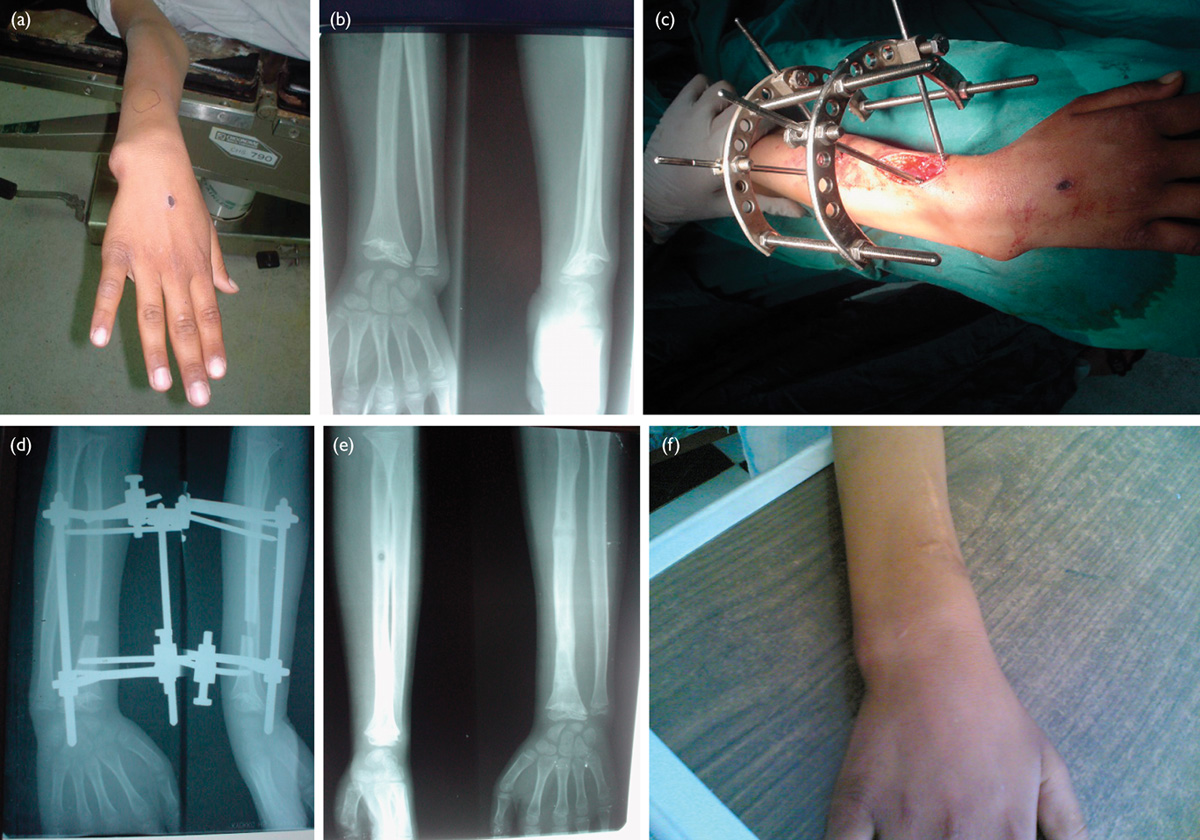
A 5-year-old patient with congenital tibial hemimelia underwent deformity correction using the Ilizarov method. Preoperative planning involved detailed analysis of the limb deformity and length discrepancy. The Ilizarov apparatus was applied, and gradual distraction was initiated. Over several months, the limb length discrepancy was corrected, and the patient achieved satisfactory alignment and function.
Case Study 2: Post-Traumatic Femoral Nonunion
A 30-year-old patient with a post-traumatic femoral nonunion and significant bone defect underwent treatment with the Ilizarov method. Following debridement of the nonunion site, the Ilizarov fixator was applied, and bone transport was performed to fill the defect. The patient achieved complete bone healing and returned to normal activities.
Clinical Outcomes
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of the Ilizarov method in achieving successful deformity correction and limb lengthening. Clinical outcomes include:
- High Success Rates: High success rates in correcting complex deformities and achieving limb length equalization.
- Functional Improvement: Significant improvement in functional outcomes and quality of life for patients.
- Minimal Recurrence: Low rates of deformity recurrence with proper postoperative care and follow-up.
Challenges and Limitations
While the Ilizarov method offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges and limitations:
Patient Compliance
- Long Treatment Duration: The extended duration of treatment and the need for regular follow-up can be challenging for patients.
- Pain and Discomfort: Discomfort associated with the external fixator and the distraction process can impact patient compliance.
Complications
- Infections: Pin site infections are a common complication that requires diligent care and monitoring.
- Neurovascular Issues: Risk of neurovascular injury during wire insertion and distraction.
- Mechanical Failures: Potential for mechanical failures, such as wire breakage or loosening.
Technical Complexity
- Surgical Expertise: Requires significant surgical expertise and experience for successful application and management.
- Resource Intensive: Resource-intensive process, requiring specialized equipment and multidisciplinary care.
Conclusion
The Ilizarov method is a powerful and versatile technique for deformity correction, offering hope to patients with complex orthopedic conditions. Its principles of distraction osteogenesis and mechanical stability have revolutionized the field of orthopedic surgery, providing solutions for conditions that

Leave a Reply